-
- Downloads
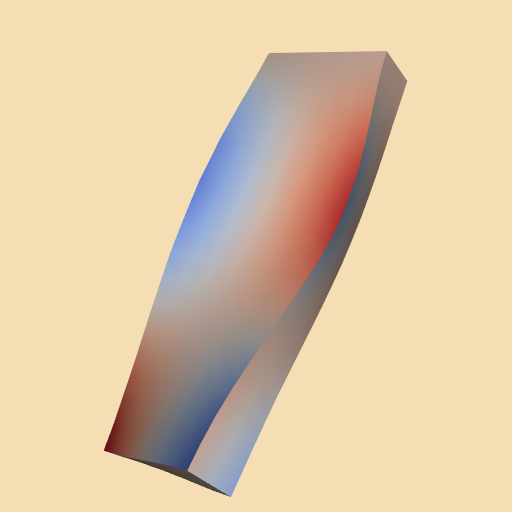
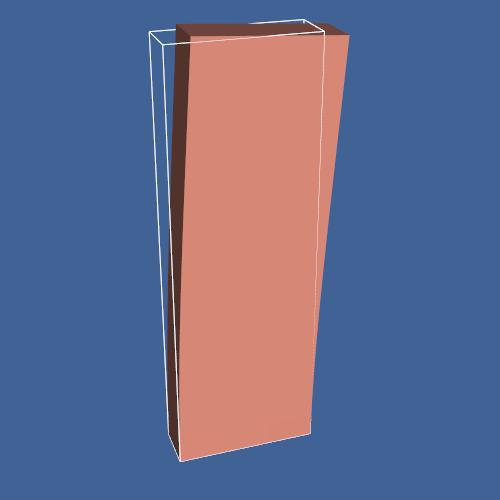
Added DisplacementPlot and PlateVibration
parent
cc055e99
No related branches found
No related tags found
Showing
- src/PythonicAPI.md 2 additions, 0 deletionssrc/PythonicAPI.md
- src/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/DisplacementPlot.md 10 additions, 0 deletionssrc/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/DisplacementPlot.md
- src/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/DisplacementPlot.py 160 additions, 0 deletionssrc/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/DisplacementPlot.py
- src/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/PlateVibration.md 6 additions, 0 deletionssrc/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/PlateVibration.md
- src/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/PlateVibration.py 86 additions, 0 deletionssrc/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/PlateVibration.py
- src/Testing/Baseline/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/TestDisplacementPlot.png 3 additions, 0 deletions...honicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/TestDisplacementPlot.png
- src/Testing/Baseline/PythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/TestPlateVibration.png 3 additions, 0 deletions...ythonicAPI/VisualizationAlgorithms/TestPlateVibration.png
130 B
129 B